HuTime Web API - Calendar Calculation
1. Overview
HuTime Web API (Calendar Calculation) provides functions to convert calendar and calculate periods based on a calendar. The API allows you to manipulate a variety of periods defined by the calendar, including not only a calendar date but also an era name, a calendar year, a calendar month or others (hereinafter, the “Calendar Period").
2. Common Item
This chapter describes the items common to all processes for use of the Web API. For items unique to each process, refer to Details of Each Process.
2-1. Basic Usage
Set a required value to each variable and submit a request by the POST or GET method to the following URL.
http://ap.hutime.org/cal/
(E.g.) Convert a calendar date on the Gregorian calendar into that on the Japanese calendar (the GET method).
http://ap.hutime.org/cal/?method=conv&ical=101.1&itype=date&ival=2017-11-16&ocal=1001.1
You can also use the API according to JSON-RPC 2.0. In this case, however, you can only use the POST method and need to set the content-type in the request header to "application/json".
(E.g.) Convert a calendar date on the Gregorian calendar into that on the Japanese calendar.
- Request:
- {"jsonrpc":"2.0","method":"conv","params":{"ocal":"1001.1","ical":"101.1","itype":"date","ival":"2017-11-17"},"id":42}
- Response:
- {"jsonrpc":"2.0","result":[{"text":"平成29年11月17日"}],"id":42}
2-2. Specifying a Calendar Period
A Calendar Period as input data should be specified either by (1) specifying a calendar resource of the Linked Data about Calendars or (2) setting necessary information for each variable. Some processes require you to set values for iuri2, ical2, itype2, ical2, and iform2 variables, in addition to the following variables.
(1) Specification by calendar resource
Set a calendar resource for the variable "iuri."
(E.g.) When specifying November 17, 2017, a calendar date on the Gregorian calendar (the same calendar date is specified in any of the following three cases):
(2) Specification by variable
Set a calendar and type of a Calendar Period, as well as a value or a character string that represents a Calendar Period for the following variables.
- ical
- Mandatory
- Specify a calendar using a Calendar ID.
- itype
- Mandatory
-
Specify a type of a Calendar Period using the following specifiers.
Specifier Type of Calendar Period date Calendar date month Calendar month year Calendar year era Era name 10y
100y
1000yPeriods of years
(Indicate 10, 100 and 1000 years, respectively.)century
millenniumCentury and millennium
(Only available in a calendar derived from the Gregorian or Julian calendar.) - ival
- Mandatory
- A character string that represents a Calendar Period (period text), or a Julian Date that indicates the beginning point of a time range.
- iform
- Optional
- Specify a date format. If "iform" is not set, the default format for each calendar applies.
(E.g.) When specifying November 17, 2017, a calendar date on the Gregorian calendar:
- ical=101.1&itype=date&ival=2017_November_17
- ical=101.1&itype=date&ival=2017-11-17
- ical=101.1&itype=date&ival=2458074.5
(3) Specifying multiple Calendar Periods
You can enter multiple Calendar Periods and process them in bulk. For specification by calendar resource, separate URIs by line breaks (CRLF) and set them in "iuri". For specification by variable, separate values that are set in "ival" by line breaks. For specification by calendar resource, each URI contains the information about calendar and type. For specification by variable, however, only one value can be set for each of "ical" and "itype". Therefore, specification by calendar resource allows you to specify multiple Calendar Period of different calendars and types, whereas specification by variable limits you to the calendar and type that are set in "ical" and "itype".
(E.g.) Specify months of March 2016, April 2016 and May 2016. "\r\n" indicates a line break.
- Specification by calendar resource:
-
iuri=http://datetime.hutime.org/calendar/101.1/month/2016-03\r\n
http://datetime.hutime.org/calendar/101.1/month/2016-04\r\n
http://datetime.hutime.org/calendar/101.1/month/2016-05 - Specification by variable:
- ical=101.1&itype=era&ival=2016-03\r\n2016-04\r\n2016-05
2-3. Information on Calendar Periods
As for information on Calendar Periods, set the following specifiers in the variable "oprop". If this setting is omitted, the API outputs a character string that represents a Calendar Period. You can also obtain multiple items by separating specifiers with ";". In this case, the output formats "text" or "tsv" deliver the multiple items in the tab-delimited style, while the "csv" format delivers them in the comma-delimited style. When the output format is "json", values are stored in the variables whose specifiers are variable names.
| Classification | Specifier | Type | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Period text | text val | Character string | A character string that represents a Calendar Period (default value) (The variable "oform" can be used to specify a format.) |
| Time range | begin | Calendar Period | A Calendar Period that indicates the beginning point of a period |
| end | Calendar Period | A Calendar Period that indicates the end point of a period | |
| jdBegin | Numerical value | A Julian Date that indicates the beginning point of a range | |
| jdEnd | Numerical value | A Julian Date that indicates the end point of a range | |
| Sequence | previous | Calendar Period | Previous Calendar Period |
| next | Calendar Period | Next Calendar Period | |
| Hierarchical relationship | ofEra | Calendar Period | A name of an era to which the date belongs |
| ofYear | Calendar Period | A calendar year to which the date belongs | |
| ofMonth | Calendar Period | A calendar month to which the date belongs | |
| Calendar resource | uri url iri | Character string | Calendar resource URI |
| label | Character string | Calendar resource label | |
| Others | dayDuration | Numerical value | Duration of a period (no. of days) |
| calendarDuration | Character string | Duration of a period (+ no. of years - no. of months - no. of days) | |
| isLeap | Boolean | Whether a Calendar Period is leap or not |
When a type of an item to be output is a Calendar Period, the output can be recursively assigned to another output item. For example, the specifier "next" of a calendar date (i.e. next day) is naturally a calendar date, which means that the calendar date can be assigned an output item to output a "calendar resource URI for the next day." In this case, use "." to connect specifiers as "next.uri". "next.next.uri" can output a "calendar resource URI for the day after 2 days." The number of specifiers that can be connected is limited to 3 in order to reduce the server load.
2-4. Outputting Results
As for the output format, set the following specifiers in the variable "out". The character code of the output data is UTF-8.
| Classification | Specifier | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Text | text |
Raw text (default value) Delimited by line breaks (CRLF) for every input data (Calendar Period). Delimited by tabs as tsv if multiple output items are specified, except that it has no title row. |
| csv | Comma-delimited text file (CSV file) Generates a record for each input data (Calendar Period). The first row is a title row. |
|
| tsv | Tab-delimited text file (TSV file) Generates a record for each input data (Calendar Period). The first row is a title row. |
|
| json | JSON data file Generates an object for each input data (Calendar Period) and returns it as an array. Each object has a variable whose name is the specifier of the output item, each of which stores a value. |
|
| RDF | rdf | Varies depending on the content-type of each request. application/json: RDF data file in the JSON format (rdf/json) Others: RDF data file in the XML format (rdf/xml) |
| rdf/xml | RDF data file in the XML format | |
| rdf/turtle | RDF data file in the turtle format | |
| rdf/json | RDF data file in the JSON format | |
| rdf/ntriple | RDF data file in the N3 format |
If the setting of the output format is omitted, the following applies depending on the setting value of the "content-type" in the request header:
- application/json: JSON data file (json)
- Other: Raw text data (text)
2-5. Handling Errors
If a process fails to be completed due to a problem with input data or other reasons, the API returns error details with HTTP status codes as shown below. JSON-RPC returns all errors as successful HTTP responses (HTTP status code: 200) and the error details are returned in the JSON format according to the JSON-RPC rules.
| Status Code | Error Details |
|---|---|
| 401 | A mandatory variable is not set or a value is invalid. |
| 404 | No corresponding Calendar Period is found (invalid specification). |
| 413 | The body length exceeds the limit during access by POST method. |
3. Details of Each Process
3-1. Obtaining Information on Calendar Periods
Based on the setting of the variable "oprop," obtain information such as a character string (period text) that represents a Calendar Period, duration, sequence, hierarchical relationship, and leap.
Variable
- method
- Mandatory
- Process type. Set "info".
- iuri or set of ical, itype, ival and iformiuri
- Mandatory
- Calendar Period whose information should be obtained. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period.
- oprop
- Optional
- Output item. For details, refer to Information on Calendar Periods.
- out
- Optional
- Output format. For details, refer to Outputting Results.
Result
Details of the items specified in the variable "oprop".
Example
"ival" has a character string representing three calendar months separated by line breaks, and they are processed in bulk. The format of the character strings to be output is set in the variable "oform" and the three calendar months, which are expressed in different formats, are integrated into a single format.
Value for each variable
method = info
ical = 101.1
itype = month
ival = 2016 Mar\r\n2016 April\r\n2016-5
oform = yyyy-MM
Result
2016-03\r\n2016-04\r\n2016-05
3-2. Converting Calendar
Convert a Calendar Period into that on a different calendar.
Variable
- method
- Mandatory
- Process type. Set "conv".
- iuri or set of ical, itype, ival and iform
- Mandatory
- A Calendar Period before conversion. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period.
- ocal
- Optional
- Specify a calendar after conversion using a Calendar ID. If this variable is omitted, the calendar after conversion will be same as the calendar before conversion.
- ep
- Optional
-
Specify either the beginning point or the ending point of the Calendar Period as a reference point for calendar conversion. If this variable is omitted, the beginning point ("b") is used.
ep Setting Value Points Used as Conversion Standard b Beginning point (default value) e Ending point be
ebBeginning point and ending point
Both results are separated by a line break (CRLF) and returned.
Output order differs between "be" and "eb". - otype
- Optional
- Specify a type of a Calendar Period after conversion. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period. If this variable is omitted, the type is the same as the calendar before conversion.
- oprop
- Optional
- Output items related to a converted Calendar Period. For details, refer to Information on Calendar Periods.
- out
- Optional
- Output format. For details, refer to Outputting Results.
Result
Details of the items specified in the variable "oprop" for a converted Calendar Period.
Example
Obtain Gregorian calendar years that correspond to the Genroku (元禄) era in Japanese Calendar. As both of the beginning point and the ending point are specified as reference points ofthe conversion (variable "ep"), the two Gregorian calendar years that correspond to the points are output separated by a line break.
Values for each variable
method = conv
ep = be
iuri = http://datetime.hutime.org/calendar/1001.1/era/元禄
ocal = 101.1
otype = year
Result
C.E. 1688\r\nC.E. 1704
3-3. Adding a Duration to a Calendar Period
Add a duration to a Calendar Period to obtain a resultant Calendar Period, such as "1 month and 15 days after March 2nd, 2016." Multiple values for either base points or added durations can be specified. If multiple values are specified for each, those durations are added to the first Calendar Period of the base points.
Variable
- method
- Mandatory
- Process type. Set "addDays" to express a duration to be added by days, or set "addCal" to express it by years + months + days.
- iuri or set of ical, itype, ival and iform
- Mandatory
- A Calendar Period used as the base point. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period.
- ical2
- Optional
- When expressing the duration to be added by years + months + days, specify a calendar used to calculate years and months using a Calendar ID. If this variable is omitted, the calendar for calculation is the same as the calendar of the Calendar Period used as the base point.
- ival2
- Mandatory
-
A duration to be added
When expressing the duration by days: A numerical value that indicates days. If a negative value is specified, it refers to earlier days.
When expressing the duration by years, months and days: Expressed as [Sign][No. of years]-[No. of months]-[No. of days] (e.g. +42-09-21: 42 years and 9 months and 21 days later). When the sign is minus ("-"), the period is backdated (e.g. -42-09-21: 42 years and 9 months and 21 days earlier). If multiple values are specified, they are separated by line breaks. - ep
- Optional
-
Specify which point to use when adding a period. If this variable is omitted, the conversion is calculated based on the beginning point of a base point to the beginning point of a target point ("bb").
ep Setting Value Points Used as Conversion Standard bb Beginning point of a base point to the beginning point of a target point (default value) ee Ending point of a base point to the ending point of a target point be Beginning point of a base point to the ending point of a target point eb Ending point of a base point to the beginning point of a target point - otype
- Optional
- Specify a type of a Calendar Period for conversion and other processing. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period. If this variable is omitted, a Calendar Period of the same type as for the base point is output.
- oprop
- Optional
- Output items. For details, refer to Information on Calendar Periods.
- out
- Optional
- Output format. For details, refer to Outputting Results.
Result
Details of the items specified in the variable "oprop" for the Calendar Period to which a duration is added.
Example
Obtain date 1 month and 15 days after March 2nd, 2016. The duration to be added is based on the Julian-Gregorian calendar (variable "ical2"). fifteen days is represented as "+0-1-15" in the order of years, months, and days (variable "ival2").
Value for each variable
method = addCal
ep = bb
ical = 101.1
itype = date
ival = 2016-03-02
ical2 = 101.1
ival2 = +0-1-15
Result
C.E. 2016 April 17
3-4. Obtaining Duration between Two Calendar Periods
Obtain duration between two Calendar Periods (from the base point to the target point). One such example is how many years, months and days there were between March 14th, 1879 and 18th April, 1955. You can specify multiple base points or target points. If multiple values are specified for each, the duration between the first base point and each of the target points is calculated.
Variable
- method
- Mandatory
- Process type. Set "durDays" to express a duration to be obtained by days, or set "durCal" to express it by years + months + days.
- iuri or set of ical, itype, ival and iform
- Mandatory
- A Calendar Period used as the base point of a period to be calculated. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period.
- iuri2 or set of ical2, itype2, ival2 and iform2
- Partially optional
- A Calendar Period used as the target point of a period to be calculated. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period. The variables "ical2" and "itype2" are optional. If these two variables are omitted, the same calendar and type of the base point are used, respectively.
- ocal
- Optional
- To express the duration to be obtained based on a calendar such as by years + months + days, specify a calendar used to calculate years and months using a Calendar ID. If this variable is omitted, the calendar for calculation is same as the calendar of the base point.
- ep
- Optional
-
Specify which point to use when calculating a period. If this variable is omitted, the beginning point of a base point to the beginning point of a target point ("bb") is used.
ep Setting Points Used for Measurement bb Beginning point of a base point to the beginning point of a target point (default value) ee Ending point of a base point to the ending point of a target point be Beginning point of a base point to the ending point of a target point eb Ending point of a base point to the beginning point of a target point - odur
- Optional
-
When expressing the duration to be obtained based on a calendar such as by years + months + days, specify a type used to express the duration. If this variable is omitted, the duration is represented as the numbers of years, months and days ("ymd").
odur Setting Type Used to Express a Period ymd ±[No. of years]-[No. of months]-[No. of days] (default value) md ±0-[No. of months]-[No. of days] yd ±[No. of years]-0-[No. of days] d ±0-0-[No. of days] - out
- Optional
- Output format. For details, refer to Outputting Results.
Result
A duration between a base point and a target point. When expressing a duration by days (method = "durDays"), its numerical value is returned. When expressing it by years, months and days (method = "durCal"), a character string representing the period is returned according to the "odur" setting. The sign becomes negative when the calculation’s target point comes before the base point.
Example
Calculate the life span of Albert Einstein (from March 14th, 1879 to 18th April, 1955). The outcome turns out to be 76 years and 1 months and 5 days. Beginning and ending points are specified in order to calculate the period of his life span.
Value for each variable
method = durCal
ep = be
ical = 101.1
itype = date
ival = 1879-03-14
ical2 = 101.1
itype2 = date
ival2 = 1955-04-18
Result
+76-1-5
3-5. Obtaining a Relative Relation between Two Calendar Periods
Obtain a relative relation between two Calendar Periods on the temporal axis based on Allen's Time Interval Algebra. You can enter multiple Calendar Periods for either A or B in the following figure. If multiple Calendar Periods are entered for both, each Calendar Period for B is compared with the first Calendar Period for A.
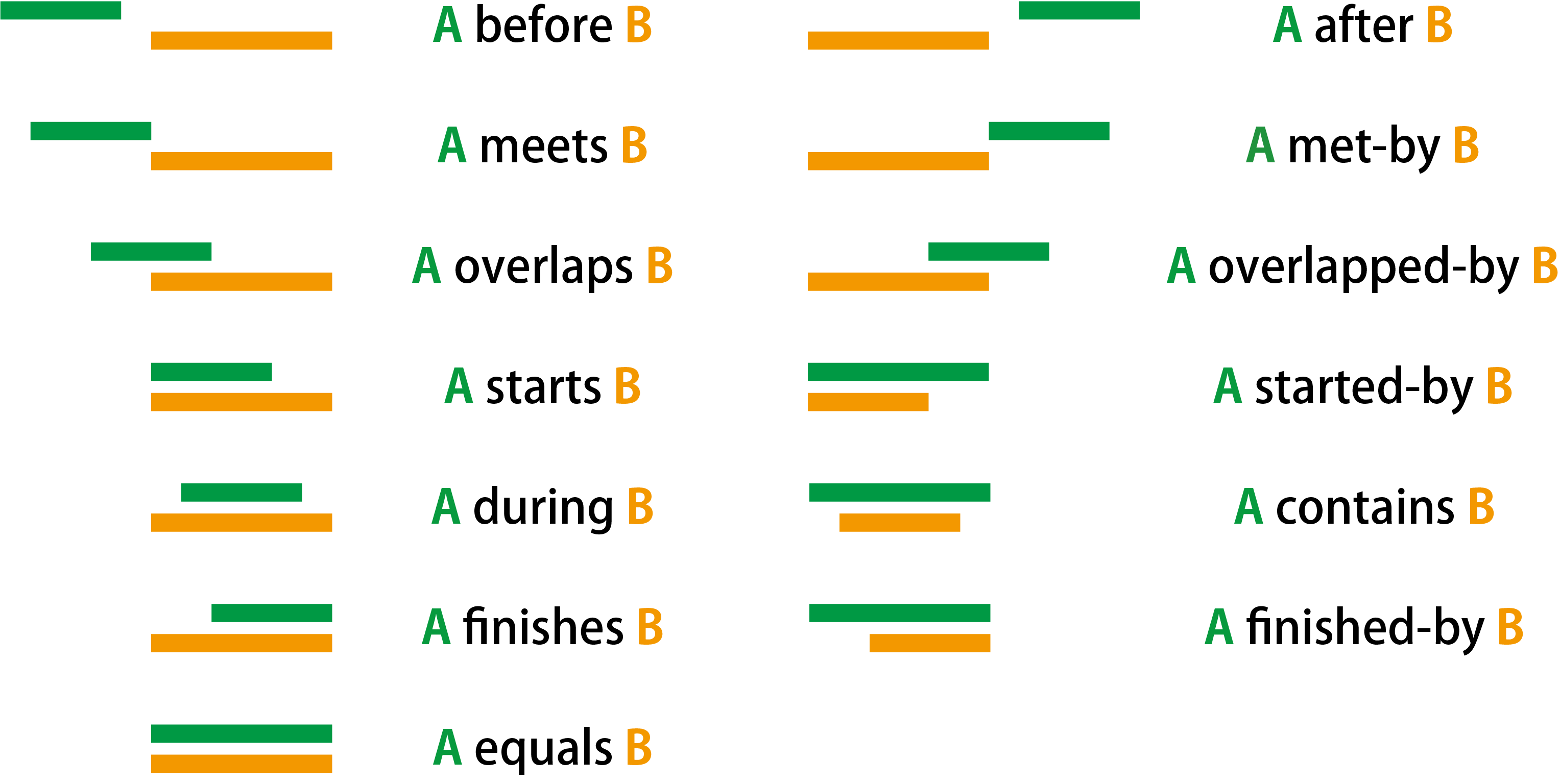
Allen's Time Interval Algebra (Allen 1983)
Variable
- method
- Mandatory
- Process type. Set "comp".
- iuri or set of ical, itype, ival and iform
- Mandatory
- A Calendar Period used as a base point of a comparison. It corresponds to A in the above figure. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period.
- iuri2 or set of ical2, itype2, ival2 and iform2
- Partially optional
- A Calendar Period used as a target point of a comparison. It corresponds to B in the above figure. For details, refer to Specifying a Calendar Period. The variables "ical2" and "itype2" are optional. If these two variables are omitted, the same calendar and type of the base point are used, respectively.
- out
- Optional
- Output format. For details, refer to Outputting Results.
Result
A relative relation between two Calendar Periods on the temporal axis. The result is returned based on Allen’s Time Interval Algebra.
Example
Obtain a relative relation between the Genroku (元禄) era (1688-1704) on the Japanese calendar and the 17th century on the Gregorian calendar. The result "OverlappedBy" indicates that the 17th century began earlier than the Genroku era, and after the two periods were overlapped, the Genroku era ended later than the 17th century.
Value for each variable
method = comp
ical = 1001.1
itype = era
ival = 元禄
ical2 = 101.1
itype2 = century
ival2 = 17
Result
OverlappedBy
4. Usage Notes
- This Web API is available for free.
- The API’s specifications and its terms of use are subject to change without notice.
- The HuTime Project and all parties concerned in the project disclaim any liability for any damages and disadvantages to any user of this Web API caused by use of the API and any change made to its specifications or its terms of use.
- When you release the outcome of your research, development or any other activity that uses this Web API, please include the clear statement of using the API.
5. References
- Sekino, T. (2017) Calendar Web API – Calendar conversion and calculation of duration. Proceedings of The Computers and the Humanities Symposium 2017: 23-28. (in Japanese)
- Sekino, T. (2017) Basic linked data resource for temporal information. Proceedings of the 2017 Pacific Neighborhood Consortium Annual Conference and Joint Meetings (PNC), IEEE Catalog Number: CFP17M10-ART:76-82.
- Sekino, T. (2015) Linked data about calendars and their usage.Proceedings of The Computers and the Humanities Symposium 2015:191-198. (in Japanese)
- Allen, J.F. (1983) Maintaining knowledge about temporal intervals. Communications of the ACM 26(11):832-843.